Counting sort is a sorting technique based on keys between a specific range. It works by counting the number of objects having distinct key values (kind of hashing). Then doing some arithmetic to calculate the position of each object in the output sequence.
Let us understand it with the help of an example.
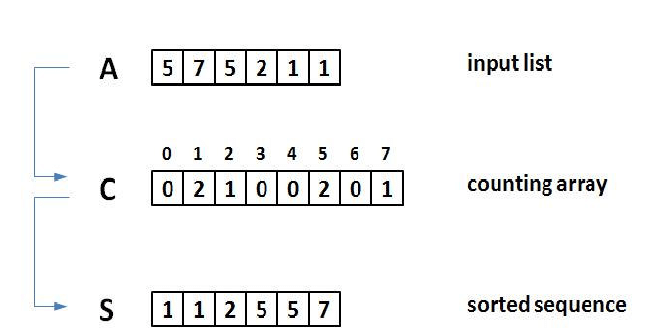
For simplicity, consider the data in the range 0 to 9. Input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2 1) Take a count array to store the count of each unique object. Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Count: 0 2 2 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 2) Modify the count array such that each element at each index stores the sum of previous counts. Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Count: 0 2 4 4 5 6 6 7 7 7 The modified count array indicates the position of each object in the output sequence. 3) Output each object from the input sequence followed by decreasing its count by 1. Process the input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2.Position of 1 is 2. Put data 1 at index 2 in output. Decrease count by 1 to place next data 1 at an index 1 smaller than this index.
# Python program for counting sort
# The main function that sort the given string arr[] in
# alphabetical order
def countSort(arr):
# The output character array that will have sorted arr
output = [0 for i in range(256)]
# Create a count array to store count of inidividul
# characters and initialize count array as 0
count = [0 for i in range(256)]
# For storing the resulting answer since the
# string is immutable
ans = ["" for _ in arr]
# Store count of each character
for i in arr:
count[ord(i)] += 1
# Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual
# position of this character in output array
for i in range(256):
count[i] += count[i-1]
# Build the output character array
for i in range(len(arr)):
output[count[ord(arr[i])]-1] = arr[i]
count[ord(arr[i])] -= 1
# Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now
# contains sorted characters
for i in range(len(arr)):
ans[i] = output[i]
return ans
# Driver program to test above function
arr = "geeksforgeeks"
ans = countSort(arr)
print "Sorted character array is %s" %("".join(ans))
Output: Sorted character array is eeeefggkkorss
Time Complexity: O(n+k) where n is the number of elements in input array and k is the range of input.
Auxiliary Space: O(n+k)
Points to be noted:
1. Counting sort is efficient if the range of input data is not significantly greater than the number of objects to be sorted. Consider the situation where the input sequence is between range 1 to 10K and the data is 10, 5, 10K, 5K.
2. It is not a comparison based sorting. It running time complexity is O(n) with space proportional to the range of data.
3. It is often used as a sub-routine to another sorting algorithm like radix sort.
4. Counting sort uses a partial hashing to count the occurrence of the data object in O(1).
5. Counting sort can be extended to work for negative inputs also.

One thought on “Counting Sort”