Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works the way we sort playing cards in our hands.
ALGORITHM
// Sort an arr[] of size n
insertionSort(arr, n)
Loop from i = 1 to n-1.
……a) Pick element arr[i] and insert it into sorted sequence arr[0…i-1]
Example1:
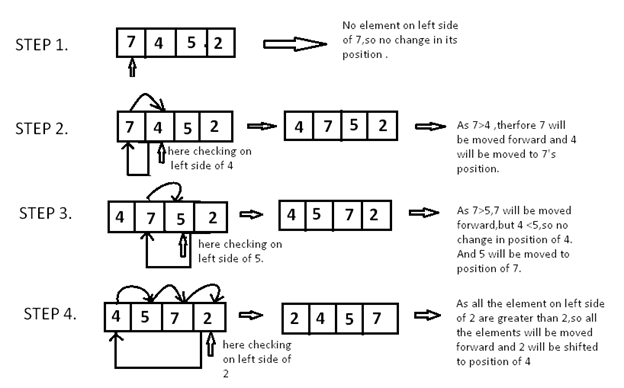
Since 7 is the first element has no other element to be compared with, it remains at its position. Now when on moving towards 4, 7 is the largest element in the sorted list and greater than 4. So, move 4 to its correct position i.e. before 7. Similarly with 5, as 7 (largest element in the sorted list) is greater than 5, we will move 5 to its correct position. Finally for 2, all the elements on the left side of 2 (sorted list) are moved one position forward as all are greater than 2 and then 2 is placed in the first position. Finally, the given array will result in a sorted array.
Example2:
12, 11, 13, 5, 6
Let us loop for i = 1 (second element of the array) to 4 (last element of the array)
i = 2. 13 will remain at its position as all elements in A[0..I-1] are smaller than 13
11, 12, 13, 5, 6
i = 3. 5 will move to the beginning and all other elements from 11 to 13 will move one position ahead of their current position.
5, 11, 12, 13, 6
i = 4. 6 will move to position after 5, and elements from 11 to 13 will move one position ahead of their current position.
5, 6, 11, 12, 13
Time Complexity: O(n*2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Boundary Cases: Insertion sort takes maximum time to sort if elements are sorted in reverse order. And it takes minimum time (Order of n) when elements are already sorted.
Algorithmic Paradigm: Incremental Approach
Sorting In Place: Yes
Stable: Yes
Online: Yes
Uses: Insertion sort is used when number of elements is small. It can also be useful when input array is almost sorted, only few elements are misplaced in complete big array.
What is Binary Insertion Sort?
We can use binary search to reduce the number of comparisons in normal insertion sort. Binary Insertion Sort uses binary search to find the proper location to insert the selected item at each iteration. In normal insertion, sorting takes O(i) (at ith iteration) in worst case. We can reduce it to O(logi) by using binary search. The algorithm, as a whole, still has a running worst case running time of O(n2) because of the series of swaps required for each insertion. Refer this for implementation.
How to implement Insertion Sort for Linked List?
Below is simple insertion sort algorithm for linked list.
- Create an empty sorted (or result) list
- Traverse the given list, do following for every node.
- Insert current node in sorted way in sorted or result list.
- Change head of given linked list to head of sorted (or result) list.
CODE
# Python program for implementation of Insertion Sort
# Function to do insertion sort
def insertionSort(arr):
# Traverse through 1 to len(arr)
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
key = arr[i]
# Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
# greater than key, to one position ahead
# of their current position
j = i-1
while j >= 0 and key < arr[j] :
arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
j -= 1
arr[j + 1] = key
# Driver code to test above
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
insertionSort(arr)
for i in range(len(arr)):
print ("% d" % arr[i])
Output: 5 6 11 12 13
Recursive Insertion Sort
Insertion sort is a simple sorting algorithm that works the way we sort playing cards in our hands.
ALGORITHM
Below is an iterative algorithm for insertion sort
// Sort an arr[] of size n
insertionSort(arr, n)
Loop from i = 1 to n-1.
a) Pick element arr[i] and insert
it into sorted sequence arr[0..i-1]
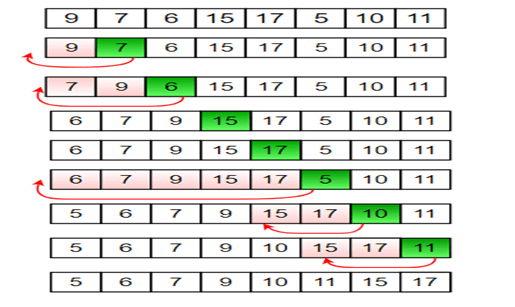
How to implement it recursively?
Recursive Insertion Sort has no performance/implementation advantages, but can be a good question to check one’s understanding of Insertion Sort and recursion.
If we take a closer look at Insertion Sort algorithm, we keep processed elements sorted and insert new elements one by one in the inserted array.
Recursion Idea.
- Base Case: If array size is 1 or smaller, return.
- Recursively sort first n-1 elements.
- Insert last element at its correct position in sorted array.
CODE
# Recursive Python program for insertion sort
# Recursive function to sort an array using insertion sort
def insertionSortRecursive(arr,n):
# base case
if n<=1:
return
# Sort first n-1 elements
insertionSortRecursive(arr,n-1)
'''Insert last element at its correct position
in sorted array.'''
last = arr[n-1]
j = n-2
# Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
# greater than key, to one position ahead
# of their current position
while (j>=0 and arr[j]>last):
arr[j+1] = arr[j]
j = j-1
arr[j+1]=last
# A utility function to print an array of size n
def printArray(arr,n):
for i in range(n):
print arr[i],
# Driver program to test insertion sort
arr = [12,11,13,5,6]
n = len(arr)
insertionSortRecursive(arr, n)
printArray(arr, n)
Output: 5 6 11 12 13


One thought on “Insertion Sort”