Searching Algorithms are designed to check for an element or retrieve an element from any data structure where it is stored. Based on the type of search operation, these algorithms are classified into 2 categories:
- Sequential Search: the list or array is traversed sequentially and every element is checked. For Ex: Linear Search.
- Interval Search: These algorithms are specifically designed for searching in sorted data-structures. These type of searching algorithms are much more efficient than Linear Search as they repeatedly target the center of the search structure and divide the search space in half. For Ex: Binary Search.
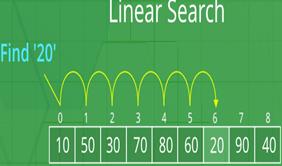

Linear Search
Linear search is a very basic and simple search algorithm. In Linear search, we search an element or value in a given array by traversing the array from the starting, till the desired element or value is found.
- The time complexity of linear search algorithm is O(n) andSpace complexity is O(1)
- It is used for unsorted small list of elements.
APPROACH
- Start from the leftmost element of arr[] and one by one compare x with each element of arr[]
- If x matches with an element, return the index.
- If x doesn’t match with any of elements, return -1.
CODE
# search x in arr[]. If x is present then return its location, else -1
def search(arr, n, x):
for i in range (0, n):
if (arr[i] == x):
return i;
return -1;
# Driver Code
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];
x = 10;
n = len(arr);
result = search(arr, n, x)
if(result == -1):
print("Element is not present in array")
else:
print("Element is present at index", %result)
Output: Element is present at index 3
Binary Search
Search a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. Begin with an interval covering the whole array. If the value of the search key is less than the item in the middle of the interval, narrow the interval to the lower half. Otherwise narrow it to the upper half. Repeatedly check until the value is found or the interval is empty.
- The time complexity of linear search algorithm is O(Log n).
- Auxiliary Space: O(1) in case of iterative implementation. In case of recursive implementation, O(Logn) recursion call stack space
- It is used in a sorted list of elements.
APPROACH:
- Compare x with the middle element.
- If x matches with middle element, we return the mid index.
- Else if x is greater than the mid element, then x can only lie in right half subarray after the mid element. So we recur for right half.
- Else (x is smaller) recur for the left half.
CODE
Recursive implementation of Binary Search
# Returns index of x in arr if present, else -1
def binarySearch (arr, l, r, x):
# Check base case
if r >= l:
mid = l + (r - l)/2
# If element is present at the middle itself
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If element is smaller than mid, then it can only be present in
#left subarray
elif arr[mid] > x:
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid-1, x)
# Else the element can only be present in right subarray
else:
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x)
else:
# Element is not present in the array
return -1
# Test array
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)
else:
print ("Element is not present in array")
Output: Element is present at index 3
Iterative implementation of Binary Search
# Search. It returns location of x in given array arr if present,
#else returns -1
def binarySearch(arr, l, r, x):
while l <= r:
mid = l + (r - l)/2;
# Check if x is present at mid
if arr[mid] == x:
return mid
# If x is greater, ignore left half
elif arr[mid] < x:
l = mid + 1
# If x is smaller, ignore right half
else:
r = mid - 1
# If we reach here, then the element was not present
return -1
# Test array
arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]
x = 10
# Function call
result = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)
if result != -1:
print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)
else:
print ("Element is not present in array")
Output: Element is present at index 3


One thought on “Search Algorithm”