The Interpolation Search is an improvement over Binary Search for instances, where the values in a sorted array are uniformly distributed. Binary Search always goes to the middle element to check. On the other hand, interpolation search may go to different locations according to the value of the key being searched. For example, if the value of the key is closer to the last element, interpolation search is likely to start search toward the end side.
- Time Complexity: If elements are uniformly distributed, then O(log(log n)). In worst case it can take upto O(n).
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
To find the position to be searched, it uses following formula. // The idea of formula is to return higher value of pos To find the position to be searched, it uses following formula. // when element to be searched is closer to arr[hi]. And // smaller value when closer to arr[lo] pos = lo + [ (x-arr[lo])*(hi-lo) / (arr[hi]-arr[Lo]) ] arr[] ==> Array where elements need to be searched x ==> Element to be searched lo ==> Starting index in arr[] hi ==> Ending index in arr[]
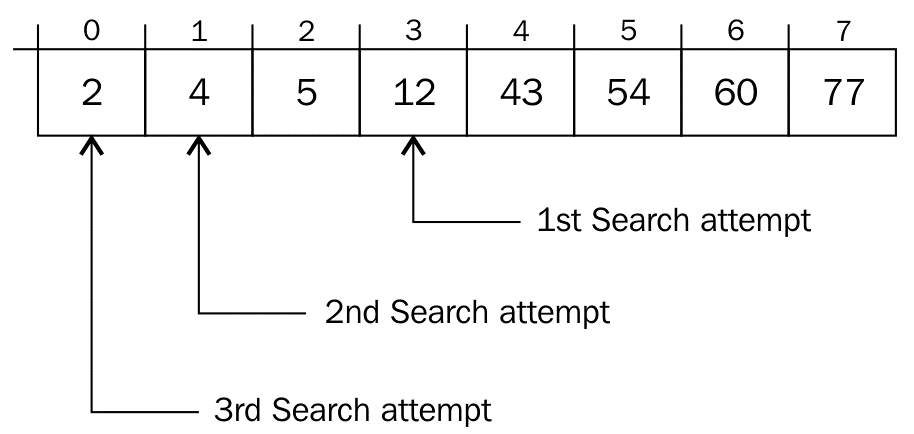
APPROACH
Rest of the algorithm is the same except the above partition logic.
Step1: In a loop, calculate the value of “pos” using the probe position formula.
Step2: If it is a match, return the index of the item, and exit.
Step3: If the item is less than arr[pos], calculate the probe position of the left sub-array. Otherwise calculate the same in the right sub-array.
Step4: Repeat until a match is found or the sub-array reduces to zero.
Below is the implementation of algorithm.
CODE
# If x is present in arr[0..n-1], then returns index of it, else returns -1
def interpolationSearch(arr, n, x):
# Find indexs of two corners
lo = 0
hi = (n - 1)
# Since array is sorted, an element present
# in array must be in range defined by corner
while lo <= hi and x >= arr[lo] and x <= arr[hi]:
if lo == hi:
if arr[lo] == x:
return lo;
return -1;
# Probing the position with keeping
# uniform distribution in mind.
pos = lo + int(((float(hi - lo) /
( arr[hi] - arr[lo])) * ( x - arr[lo])))
# Condition of target found
if arr[pos] == x:
return pos
# If x is larger, x is in upper part
if arr[pos] < x:
lo = pos + 1;
# If x is smaller, x is in lower part
else:
hi = pos - 1;
return -1
# Driver Code
# Array of items in which search will be conducted
arr = [10, 12, 13, 16, 18, 19, 20, 21, \
22, 23, 24, 33, 35, 42, 47]
n = len(arr)
x = 18 # Element to be searched
index = interpolationSearch(arr, n, x)
if index != -1:
print "Element found at index",index
else:
print "Element not found"
Output: Element found at index 4


One thought on “Interpolation Search”